Abstract
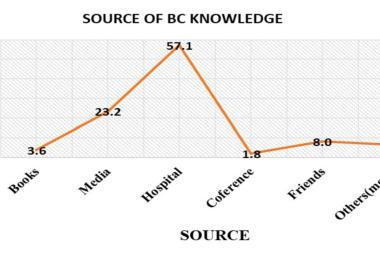
Eosinophil-type nasal polyp (NP) is common in Western population. This aim of this study was to determine the histology type of NP among different Malaysian ethnic groups. A total of 122 chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis (CRSwNP) patients were retrospectively enrolled and demographic data was recorded. The histological slides were retrieved. The number of eosinophils and non-eosinophils were counted and average number of inflammatory cells for each high power field was calculated. Eosinophil-predominant was seen in 32.8% of patients and 67.2% was non-eosinophil-predominant. Phenotypes of NP significantly showed an association with ethnicity (x² = 8.322; p < 0.05). A total of 78.9% of Chinese nasal polyps showed non-eosinophil predominant, while Malay and Indian nasal polyps revealed 71.9% and 40.7% of non-eosinophilic phenotype, respectively. Our study showed that Malaysian population had a non-eosinophilic phenotype of nasal polyps. There was a significant association in Malaysian ethnicity with the highest percentage in Chinese population.
Keywords :
eosinophil,
histology,
polyps,
Abstrak
Polip hidung jenis eosinofil biasa terjadi dalam populasi Barat. Tujuan utama kajian ini adalah untuk menentukan jenis histologi polip hidung dalam kalangan kumpulan etnik di Malaysia. Data demografi 122 pesakit yang mengidap kronik rinosinusitis dan mempunyai polip di dalam hidung mereka telah dikenalpasti dan direkod. Kepingan histologi untuk sampel polyp hidung telah dikumpulkan. Bilangan eosinofil dan bukan eosinofil serta purata sel-sel inflamasi yang terlibat dikira. Kecenderungan sel eosinofil didapati sebanyak 32.8% dan bukan eosinofil adalah sebanyak 67.2%. Jenis histologi polip hidung menunjukkan sangat signifikan di antara kaum (x² = 8.322; p < 0.05). Sebanyak 78.9% polip hidung dari kaum Cina adalah bukan eosinofil, sementara peratusan bagi kaum Melayu dan India masing-masing adalah 71.9% dan 40.7%. Kajian ini menunjukkan kecenderungan polip hidung di dalam populasi Malaysia adalah jenis bukan eosinofil dan ianya sangat signifikan bagi kaum Cina.
Kata Kunci :
eosinofil,
histology,
polip,
Correspondance Address
Salina Husain, Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, Jalan Yaacob Latif, Bandar Tun Razak, 56000 Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Tel: +60391456045 Fax: +60391456675 Email: drsalina_h@yahoo.com