The Incidence of Mandibular Second Molar Distal Caries Associated with Impacted Mandibular Third Molar: A Retrospective Study and Management Guidelines
Impacted Third Molar, Prophylactic Removal
Abstract
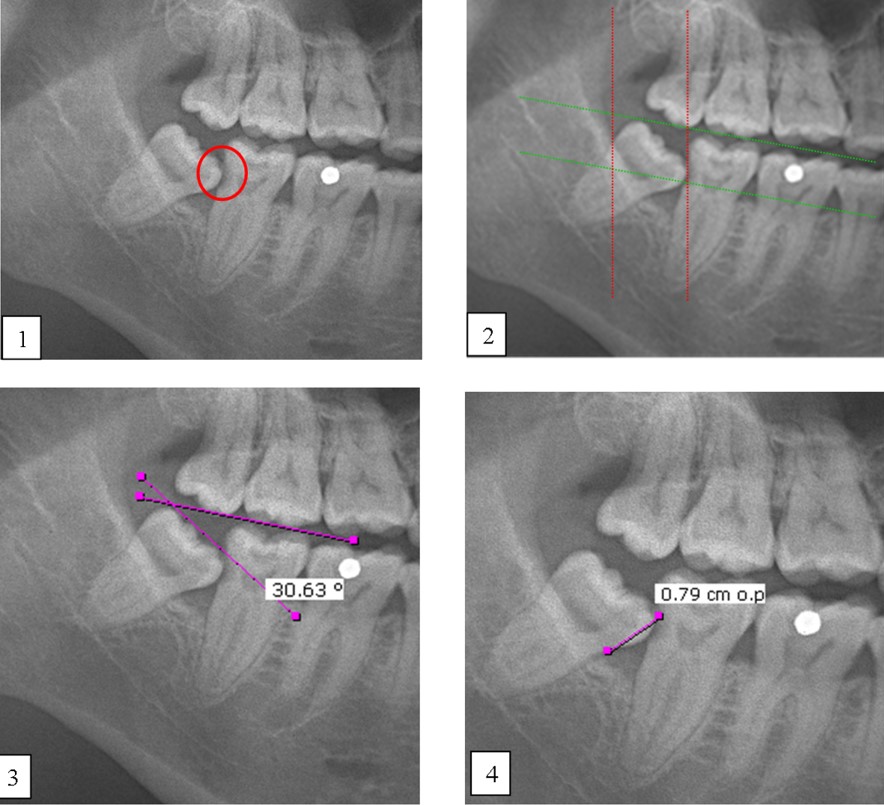
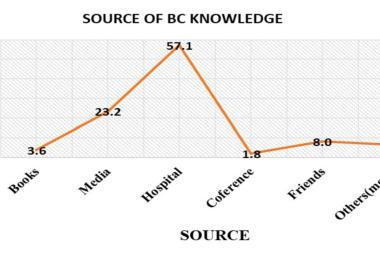
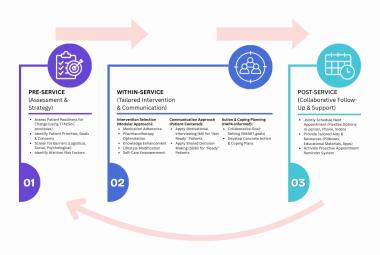
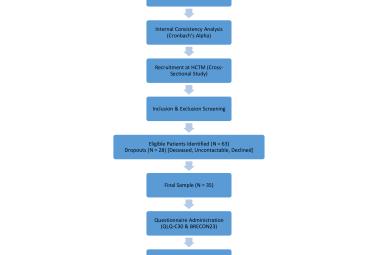
One of the notable complications of impacted mandibular third molar (MTM) is distal caries of the mandibular second molar (MSM) which can eventually lead to its early loss. The present study aimed to investigate the incidence of dental caries in MSM associated with impacted MTM and to propose an assessment protocol for MTM management. Patients’ dental records with dental panoramic tomography (DPT) imaging were studied retrospectively, in total 583 MTM images were evaluated. The presence of MSM distal caries, patient’s details, impaction depth, pattern and angulation of MTM and the distances between distal MSM and mesial MTM were assessed. Logistic regression analysis was performed on the data set. The highest caries incidence was observed in mesioangular impacted MTM (34.1%). Majority of the caries found were Level A (27.9%) and Class II (27.0%). The highest distance between distal MSM and MTM contributing to caries was 0.70-0.99 cm (31.9%). Patients’ age, angulation, pattern and depth of impacted MTM are the predictors which significantly increase the caries incidence in MSM (p<0.05). Prophylactic removal of MTM should be proposed when the distance of mesial impacted MTM and distal MSM is around 0.70-0.99 cm, and is mesially angulated with IIA classification.
Keywords :
Caries incidence; dental caries; impacted third molar; mandibular second molar; prophylactic removal,
Abstrak
Salah satu komplikasi ketara gigi geraham bongsu rahang bawah (MTM) yang tidak tumbuh sepenuhnya (terimpak) ialah karies distal pada geraham kedua rahang bawah (MSM) yang akhirnya boleh menyebabkan kehilangan awal gigi tersebut. Kajian ini bertujuan untuk menyiasat kejadian karies gigi pada MSM yang mempunyai kaitan dengan MTM terimpak serta cadangan penilaian langkah pengurusan berkaitan dengan MTM. Rekod pergigian pesakit bersama gambar panoramik pergigian telah dikaji secara retrospektif, dengan sejumlah 583 imej MTM telah dinilai. Kewujudan karies distal MSM, butiran pesakit, kedalaman impaksi, corak dan sudut MTM serta jarak antara MSM distal dan MTM mesial telah dinilai. Analisis regresi logistik dijalankan ke atas set data. Insiden karies tertinggi diperhatikan pada MTM terimpak mesioangular (34.1%). Kebanyakan karies yang ditemui ialah Tahap A (27.9%) dan Kelas II (27.0%). Jarak tertinggi antara MSM distal dan MTM yang menyumbang kepada karies ialah 0.70-0.99 cm (31.9%). Umur pesakit, sudut, corak dan kedalaman MTM terimpak ialah pembolehubah yang meningkatkan insiden karies pada MSM secara signifikan (p<0.05). Cabutan pencegahan gigi MTM sepatutnya dicadangkan apabila jarak antara MTM terimpak mesial dan MSM distal adalah sekitar 0.70-0.99 cm, dan MTM bersudut mesial dengan klasifikasi IIA.
Kata Kunci :
Cabutan pencegahan; geraham kedua bawah; geraham ketiga terimpak; karies gigi; kejadian karies,
Correspondance Address
Nora Sakina Mohd Noor. Department of Restorative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Universiti Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Tel: +60379676488 / +60379674814 Email: norasakina@um.edu.my