A Suprise Diagnosis of Parapharyngeal Cavernous Hemangioma in an Adult
Parapharyngeal Cavernous Hemangioma in an Adult
Abstract
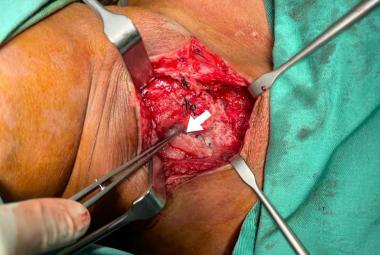
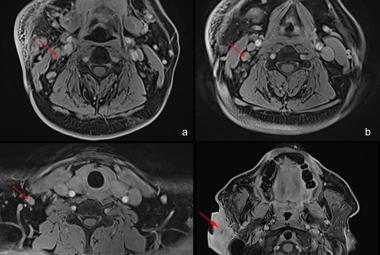
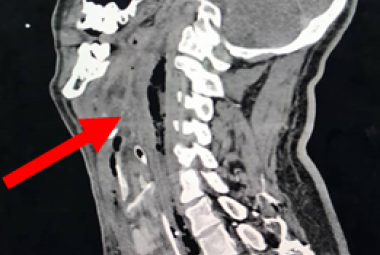
Parapharyngeal space contains many vital structures thus various pathology may arise from this region. Hemangiomas are benign rare vascular tumors that are histologically categorised as capillary, cavernous and mixed capillary. We were reporting a rare case of a cavernous hemangioma in the parapharyngeal space. There are various diagnostic approaches in diagnosis of cavernous hemangioma. Imaging such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is better than computed tomography (CT) scan. However, in this case we proceeded with contrasted CT scan where it showed well defined enhancing mass at the left parapharyngeal space with close proximity to the carotid artery. Asymptomatic cavernous hemangioma can be treated conservatively. Depending on the sites of the tumor, other treatment modalities that can be used such as systemic steroids, radiation, pre operative embolisation or scelerosing agents. Complete excision is the best in treating cavernous hemangiomas to prevent the recurrent of the disease. Hemangiomas should be considered as one of the differentials if a mass of soft tissue lesion with high vascularity been revealed by imaging. In this case, there was a diagnostic dilemma. Parapharyneal hemangioma should be one of the differential diagnosis for any neck swelling over the parapharyngeal space. Complete excision of the tumor brings about the best favourable outcome, with a lower recurrence rate even without preoperative embolisation.
Keywords :
Cavernous,
hemangioma,
parapharyngeal tumour,
vascular tumour,
Abstrak
Ruang parafaring mengandungi banyak struktur penting. Oleh itu, pelbagai jenis patologi mungkin timbul daripada bahagian ini. Hemangioma ialah tumor vaskular yang jarang dan tidak merbahaya. Secara histologi, tumor ini boleh dikategorikan sebagai kapilari, kavernosus dan kapilari campuran. Terdapat pelbagai jenis pendekatan diagnostik dalam membuat diagnosis hemangioma kavernosus. Pengimejan seperti pengimejan resonans magnet (MRI) adalah lebih baik daripada imbasan tomografi berkomputer (CT). Walau bagaimanapun, dalam kes ini kami meneruskan dengan imbasan CT kontras di mana ia menunjukkan jisim peningkatan yang jelas di ruang parafaring kiri dengan berdekatan dengan arteri karotid. Kebanyakan hemangioma tanpa gejala boleh dirawat secara konservatif. Namun, ia bergantung kepada jenis tumor. Kaedah rawatan lain yang boleh digunakan untuk merawat hamangioma kavernous seperti steroid sistemik, sinaran, embolisasi pra operasi atau agen skelerosan. Secara kesimpulan, rawatan yang paling baik adalah dengan mengeluarkan kesuluruhan tumor secara pembedahan. Dalam kes ini terdapat dilema diagnostik. Hemangioma parafaring harus menjadi salah satu diagnosis berbanding tumor-tumor lain untuk sebarang pembengkakan leher di ruang parapharyngeal. Pembedahan untuk mengeluarkan keseluruhan tumor ini dapat memberi hasil terbaik daripada ia tumbuh berulang kali tanpa embolisasi praoperasi.
Kata Kunci :
Hemangioma,
kavernous,
tumor parafaring,
tumor vaskular,
Correspondance Address
Vishnu Moganadass. Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Jalan Yaacob Latif, Bandar Tun Razak, 56000 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Tel: +6019-6689065 Email: m.vishnuvarathan@yahoo.com