Risk Determinants of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus Attending Follow-Up Clinics at University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Center (UKMMC): A Cross Sectional Study
Peripheral neuropathy and Type II diabetes
Abstract
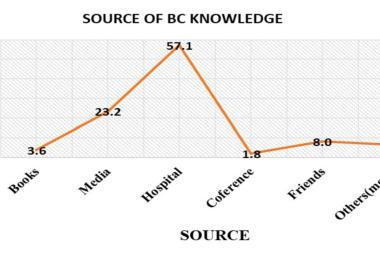
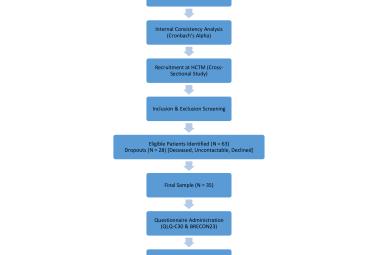
Peripheral neuropathy is highly associated with foot complications among diabetics. This study aimedto identify risk factors associated with the development of peripheral neuropathy in diabetic patients and their association with degree of severity of peripheral neuropathy. Across-sectional study was conducted in follow-up clinics at the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre (UKMMC), Malaysia involving 72 diabetic patients and 19 controls. Exclusion criteria were those with amputated limbs, gross foot deformity and existing peripheral neuropathy. Controls were non diabetics who walked normally, had no history of foot problem and attended the clinic as subjects’ companion. Quantitative assessment of neuropathy was done using Semmes-Weinstein monofilament. Neuropathy Disability Score (NDS) were used to quantify severity of diabetic neuropathy. Spearman’s Rank test and Mann-Whitney test were used to determine correlation between variables and their differences. Logistic regression analysis was used to determine risk factors associated with peripheral neuropathy. The mean HbA1c among diabetics was 8.6% + 4.1, and mean NDS was 7.0 + 6.0. A total of 79.1% demonstrated various level of neuropathy with presence of callus was associated with higher NDS scores. Older age (P=0.02), body weight (P=0.03), HbA1c (P=0.005) and duration of diabetes (P <0.005) showed positive correlation with NDS. Proper foot care program for diabetics should include recognition of the callus, with special emphasis given to those with heavier weight and increasing age.
Keywords :
callus,
Diabetes mellitus,
Neuropathy Disability Score (NDS),
peripheral neuropathy,
Semmes Weinstein monofilament (SWMF),
Abstrak
Neuropati periferi adalah berkait rapat dengan masalah kaki di kalangan penghidap diabetes melitus. Kajian ini bertujuan untuk mengenalpasti tahap neuropati dan faktor-faktor risiko berkaitan dengan keadaan ini. Satu kajian hirisan lintang telah dijalankan di klinik-klinik ulangan Pusat Perubatan UKM (PPUKM) Malaysia, melibatkan 72 pesakit diabetes dan 19 pesakit kawalan. Pesakit yang mempunyai kaki yang bermasalah dan telah mempunyai neuropati tidak dimasukkan dalam kajian. Pesakit kawalan dipilih dari mereka yang tidak mempunyai diabetes, boleh berjalan secara normal, tiada masalah dengan kaki serta menghadiri klinik sebagai peneman kepada pesakit. Kajian kuantitatif dilakukan menggunakan Semmes-Weinstein monofilamen. ‘Neuropathy Disability Score’ (NDS) digunakan untuk mengukur tahap neuropati diabetes. Ujian ‘Spearman rank’ dan ‘Mann-whitney’ dijalankan bagi mengenalpasti hubungkait antara neuropati dan faktor-faktor yang dikaji. Ujian ‘logistic regression’ dijalankan untuk mengenalpasti faktor risiko keadaan ini. Aras purata HbA1c pada pesakit ialah 8.6 + 4.1, dan purata NDS ialah 7.0 + 6.0. Sejumlah 79.1% didapati mempunyai neuropati dalam berbagai tahap, dengan faktor kalus kaki dikenalpasti berhubungkait dengan markah NDS yang tinggi. Faktor lanjut usia (p = 0.02), berat badan (p = 0.03), HbA1c (p = 0.005) dan jangkamasa menghidap diabetes (p = < 0.005) mempunyai hubungkait positif dengan NDS. Program penjagaan kaki yang teratur untuk pesakit diabetes perlu mengambil kira faktor kalus kaki, dengan keutamaan diberi kepada mereka yang mempunyai berat badan berlebihan dan telah lanjut usia.
Kata Kunci :
'Neuropathy Disability Score (NDS)',
'Semmens-Weinstein monofilamen(SWMF),
diabetes melitus,
kalus,
neuropati periferi,
Correspondance Address
Assoc Prof Dr Noor Azah Aziz, Department of Family Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Jalan Yaacob Latif, Bandar Tun Razak, 56000 Cheras, Kuala Lumpur. Tel: 603-9145 6116. Fax: 603-9173 8153. Email: azah@ppukm.ukm.my