The Outcome of Medical Treatment of Endometrial Hyperplasia
Medical Treatment in Endometrial Hyperplasia
Abstract
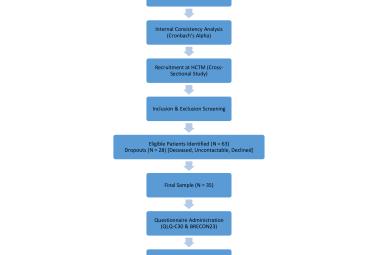
Endometrial hyperplasia (EH) poses significant challenges in clinical management, particularly concerning the choice of medical modalities and their efficacy in achieving symptom resolution and regression of hyperplastic changes. To address this, we conducted a retrospective study at Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz (HCTM) to investigate the outcomes of various medical treatments for EH with/without atypia over a 10-year period from 2007 to 2017. Patient’s clinical background and endometrial tissue biopsy results were obtained from medical records and histopathological laboratory respectively. We analysed the type and duration of medical treatments, as well as symptoms regression and outcome of the treatments. A total of 86 women received treatment for EH with average age of 48.2 + 12.3 (median 46) years. Of these, 65 (75.6%) had EH without atypia, and 21 (24.4%) had atypical EH. All women had their symptoms resolved in less than 6 months of treatment, with varying duration depending on different regimes used. Levonogestrel-intrauterine system (LNG-IUS) had symptoms resolved by 3 to 6 months (p<0.01) while intramuscular Medroxyprogesterone Acetate (MPA) (2 in 86) had resolution of symptoms in less than 3 months. Gonadotropin-releasing Hormone (GnRH) analogue and oral progestogen had different duration of response rate between 0-6 months. LNG-IUS failed to achieve endometrial regression in 12.5% and 23.3% with oral progestogen. LNG-IUS, GnRH analogue and MPA had acceptable regression rate of EH. Oral progestogen had the highest failure rate in achieving EH regression. This is likely due to compliance issue with oral treatment.
Keywords :
Endometrial hyperplasia,
gonadotrophin,
intrauterine system,
medroxyprogesterone acetate,
progestogen,
Abstrak
Terdapat pelbagai cabaran dalam pengurusan klinikal hiperplasia endometrium (EH), terutamanya berkaitan dengan pemilihan kaedah perubatan dan keberkesanannya dalam mencapai penyelesaian simptom dan regresi perubahan hiperplastik. Untuk menangani masalah ini, kami telah menjalankan satu kajian retrospektif di Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz (HCTM) untuk menyiasat hasil pelbagai rawatan perubatan untuk EH dengan/tanpa atipia selama tempoh 10 tahun dari 2007 hingga 2017. Maklumat latar belakang klinikal pesakit dan keputusan biopsi tisu endometrium mereka diperolehi daripada rekod perubatan dan makmal histopatologi. Kami menganalisis jenis dan tempoh rawatan perubatan, regresi simptom, dan hasil rawatan tersebut. Sebanyak 86 wanita telah menerima rawatan untuk EH dengan purata umur 48.2 + 12.3 (median 46) tahun. Dari jumlah ini, 65 (75.6%) mengalami EH tanpa atipia, dan 21 (24.4%) mengalami EH atipia. Semua wanita mendapati simptom mereka pulih dalam tempoh kurang dari 6 bulan rawatan, dengan tempoh yang berbeza bergantung kepada regimen yang digunakan. Sistem levonorgestrel-intrauterine (LNG-IUS) memulihkan simptom dalam tempoh masa 3 hingga 6 bulan (p<0.01) manakala Medroxyprogesterone Acetate (MPA) intramuskular (2 daripada 86) mempunyai resolusi simptom dalam tempoh kurang dari 3 bulan. Analog Hormon Pelepasan Gonadotrofin (GnRH) dan progestogen oral mempunyai tempoh tindak balas yang berbeza antara 0-6 bulan. LNG-IUS gagal mencapai regresi endometrium dalam 12.5% dan 23.3% dengan progestogen oral. LNG-IUS, analog GnRH, dan MPA mempunyai kadar regresi EH yang boleh diterima. Progestogen oral mempunyai kadar kegagalan tertinggi dalam mencapai regresi EH. Ini mungkin disebabkan oleh isu pematuhan dengan rawatan oral.
Kata Kunci :
Gonadotropin,
hiperplasia endometrium,
medroxyprogesterone acetate,
progestogen,
sistem intrauterin,
Correspondance Address
Mohamad Nasir Shafiee, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Jalan Yaacob Latif, Bandar Tun Razak, 56000 Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Tel: +603-9145 5949 / 5950 Email: nasirshafiee@hotmail.com / nasirshafiee@ukm.edu.my