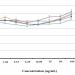
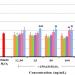
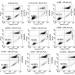
Oxidative stress-induced neuronal damage, mediated by the cellular accumulation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), was reported to be involved in neurodegenerative diseases. Rice and corn may serve as sources of antioxidants with the presence of phytochemicals such as melatonin and tryptophan, for fighting against reactive oxygen species (ROS). Melatoninis are known to upregulate the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene for enhancement of the nerve cell function and mediation of the anti-aging effect of the brain cells. The present study aimed at determining the effect of white rice, brown rice, black glutinous rice, sweet corn and baby corn extracts against H2O2-induced neurotoxicity and their underlying mechanisms in the mouse hippocampal HT22 cells. Following pretreatment of the HT22 cells with individual extract for 24 hrs and subsequent challenge with H2O2 for 24 hrs, cell viability, apoptosis, intracellular ROS and BDNF gene expression were measured. Rice and corn extracts were evaluated for their antioxidant activities and the levels of tryptophan and melatonin. Characteristic zed of H2O2-induced neurotoxicity included decreased cell viability, increased cellular ROS and decreased BDNF expression. Pretreatment with rice and corn extracts significantly attenuated H2O2-induced neurotoxicity, and also significantly decreased ROS production. Pretreatment with these extracts could also upregulate the expression of BDNF mRNA and protein, which may be contributed by their melatonin and tryptophan contents. Therefore, rice and corn extracts may protect HT22 cells against H2O2-induced neurotoxicity by inhibition of ROS production and modulation of BDNF expression.
Neuroprotective Effect of Rice and Corn Extracts Against H2O2-Induced Neurotoxicity in HT22 Murine Hippocampal Neuronal Cells
Author
Abstrak
Kerosakan neuron aruhan stress oksidatif yang disebabkan oleh akumulasi hydrogen peroksida (H2O2) dalam sel, telah ditunjukkan terlibat dalam penyakit neurodegeneratif. Beras dan jagung boleh menjadi sumber anti-oksidan dengan kehadiran fitokimia seperti melatonin dan triptofan untuk melawan sepsis reaktif oksigen (ROS). Melatonin telah diketahui boleh meningkatkan ekspresi gen brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) untuk merangsang fungsi sel saraf dan mengawal-atur kesan anti-penuaan oleh sel otak. Kajian ini bertujuan untuk menentukan kesan beras putih, beras perang, pulut hitam, jagung manis dan ‘baby corn’ terhadap neurotoksisiti aruhan H2O2 dan mekanisme terlibat dalam sel hipokampus HT22 mencit. Selepas sel HT22 menerima prarawatan ekstrak individu selama 24 jam dan seterusnya menerima cabaran dengan H2O2 selama 24 jam, kebolehhidupan sel, apoptosis, ROS intrasel dan ekspresi gen BDNF diukur. Ekstrak beras dan jagung dinilai untuk aktiviti anti-oksidan dan aras triptofan dan melatonin. Ciri-ciri neurotoksisiti aruhan H2O2 termasuk penurunan kebolehhidupan sel, peningkatan selular ROS dan penurunan ekspresi BDNF. Pra-rawatan dengan ekstrak beras dan jagung mengurangkan secara signifikan neurotoksisiti aruhan H2O2, dan juga mengurangkan secara signifikan pengeluaran ROS. Pra-rawatan dengan extrak-ekstrak tersebut berupaya juga untuk meningkatkan ekspresi mRNA dan protin BDNF yang mungkin disumbang oleh kandungan melatonin dan triptofan. Oleh itu, ekstrak beras dan jagung mungkin melindungi sel HT22 dari neurotoksisiti aruhan H2O2 dengan merencat pengeluaran ROS dan modulasi ekspresi BDNF.