Vestibulotoxicity Assessment using Video Head Impulse Test (v-HIT) in Cancer Patients Receiving Platinum-Based Chemotherapy at Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz
Vestibulotoxicity, Video-HIT, Chemotherapy
Abstract
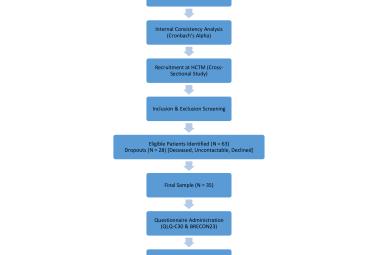
The aim of the research was to study vestibulotoxicity among cancer patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy agents, using video Head Impulse Test (v-HIT). A total of 23 patients were recruited throughout July 2020 until December 2022 from the Oncology and Haematology Unit in Hospital Censelor Tuanku Muhriz. History taking, otoscopy and visual assessments were performed. Vestibular assessments were performed with v-HIT prior to initiation of chemotherapy, post treatment and one month after treatment completion. Pre-chemotherapy vestibular assessment was performed in 23 cancer patients who received treatment. Eight (34.8%) patients were able to complete the assessments conducted. Five (21.7%) patients were able to complete assessments at treatment completion. Ten (43.5%) patients were unable to complete the assessments due to disease progression/ death. Two out of 13 (15.4%) patients who completed the assessments had decreased vestibulo-ocular reflex gain. In our study, vestibulotoxicity based on decrease in vestibulo-ocular reflex gain was 15.4% (2/13). Age was one of the factors that might cause decrease in vestibulo-ocular reflex gain. The type of cancer might also affect the vestibular function due to hormonal changes. In conclusion, this study found that 15.4% of cancer patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy exhibited vestibulotoxicity as evidenced by decreased vestibulo-ocular reflex gain on v-HIT. Age and cancer type may contribute to this risk, highlighting the need for careful vestibular monitoring in this population.
Keywords :
Chemotherapy; hearing loss; vestibulotoxicity; vestibulo-ocular reflex gain; video head impulse test,
Abstrak
Matlamat kajian ini adalah untuk mengkaji vestibulotoksisiti dalam kalangan pesakit kanser yang menerima ejen kemoterapi berasaskan platinum, menggunakan ujian video Head Impulse Test (v-HIT). Sebanyak 23 orang pesakit telah direkrut sepanjang tempoh Julai 2020 hingga Disember 2022 dari Unit Onkologi dan Hematologi di Hospital Censelor Tuanku Muhriz. Pengambilan sejarah pesakit, otoskopi dan penilaian visual telah dilakukan. Penilaian vestibular menggunakan v-HIT dilakukan sebelum memulakan kemoterapi, selepas rawatan dan sebulan selepas rawatan selesai. Penilaian vestibular prarawatan kemoterapi telah dijalankan ke atas 23 pesakit kanser yang menerima rawatan. Lapan (34.8%) pesakit berjaya melengkapkan semua penilaian yang dijalankan. Lima (21.7%) pesakit dapat melengkapkan penilaian semasa rawatan selesai. Sepuluh (43.5%) pesakit tidak dapat melengkapkan penilaian disebabkan oleh perkembangan penyakit atau kematian. Dua daripada 13 (15.4%) pesakit yang berjaya melengkapkan penilaian menunjukkan penurunan dalam refleks vestibulo-okular. Dalam kajian ini, kadar vestibulotoksisiti berdasarkan penurunan refleks vestibulo-okular adalah sebanyak 15.4% (2 daripada 13 pesakit). Faktor umur ialah salah satu faktor yang mungkin menyumbang kepada penurunan dalam keuntungan refleks vestibulo-okular. Jenis kanser juga boleh mempengaruhi fungsi vestibular akibat daripada perubahan hormon. Sebagai kesimpulan, kajian ini mendapati bahawa 15.4% pesakit kanser yang menerima kemoterapi berasaskan platinum menunjukkan “vestibulotoxicity” yang dibuktikan melalui penurunan gain refleks vestibulo-okular pada v-HIT. Faktor umur dan jenis kanser mungkin menyumbang kepada risiko ini, sekali gus menekankan keperluan pemantauan fungsi vestibular yang teliti dalam populasi ini.
Kata Kunci :
Kehilangan pendengaran; kemoterapi,
keuntungan refleks vestibulo-okular; ujian impuls kepala video; vestibulotoksisiti,
Correspondance Address
Zara Nasseri. Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Jalan Yaacob Latif, Bandar Tun Razak, 56000 Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Tel: +6012-4841322 Email: zaranasseriwork@gmail.com